Rent with confidence
Screen applicants, find the ideal tenant for your rental unit, and ensure your rental payments are guaranteed every month.

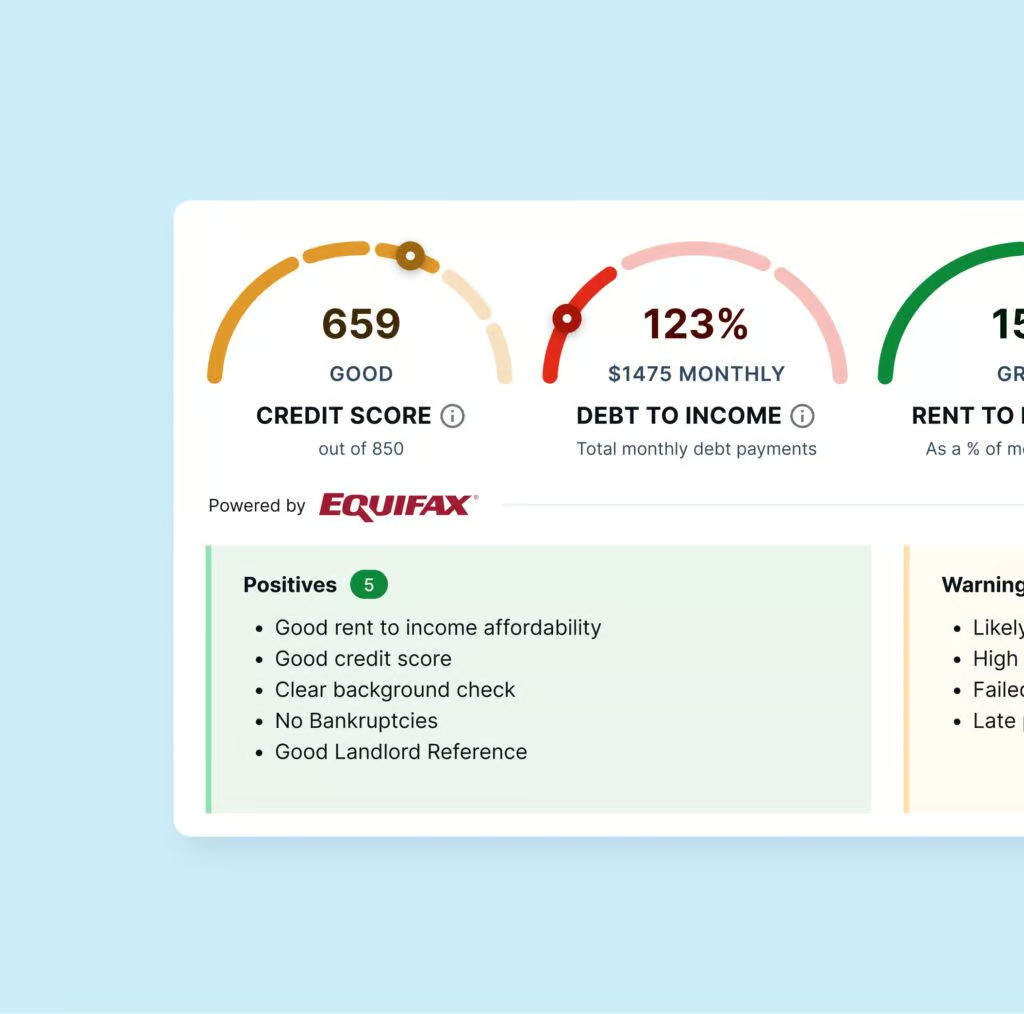
Combine a full credit check by Equifax® with employment and income info for a comprehensive picture of your potential renters
Easy, mobile friendly, and comprehensive online rental application form
We will contact your tenant’s references and share a recording and summary of the call
Includes SSN Trace, National Criminal & Sex Offender Registry Checks, and Global Sanctions Watchlist
AI-powered scan of income documents to detect signs of tampering or fraud
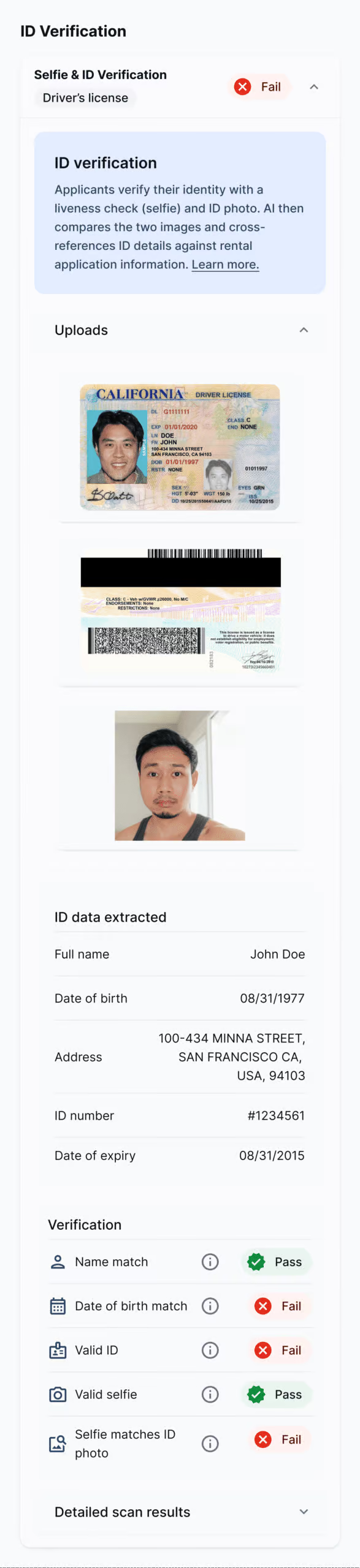
Confirm a tenant’s identity with AI-powered ID verification and liveness check
Conversations on real estate trends and property management strategies
Local tools and resources to help you manage your rental property successfully
Learn how to solve renting challenges from our experts
Articles on how to navigate the in-app SingleKey experience



















Used by teams at:


















Screen and manage risks all in one integrated platform.
Combine a full credit check by Equifax® with in-depth, employment and income info to get a comprehensive picture of your potential renters.
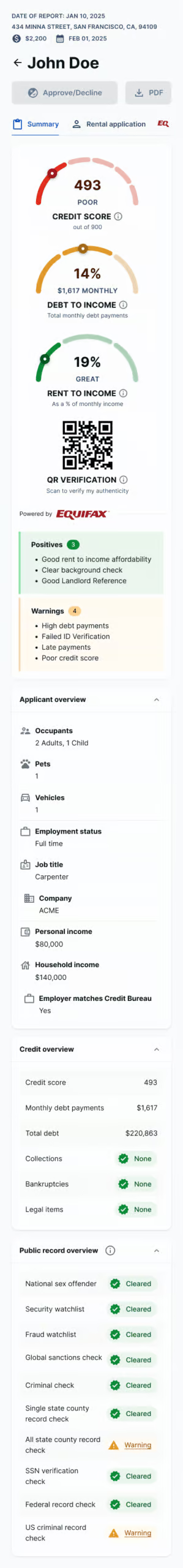


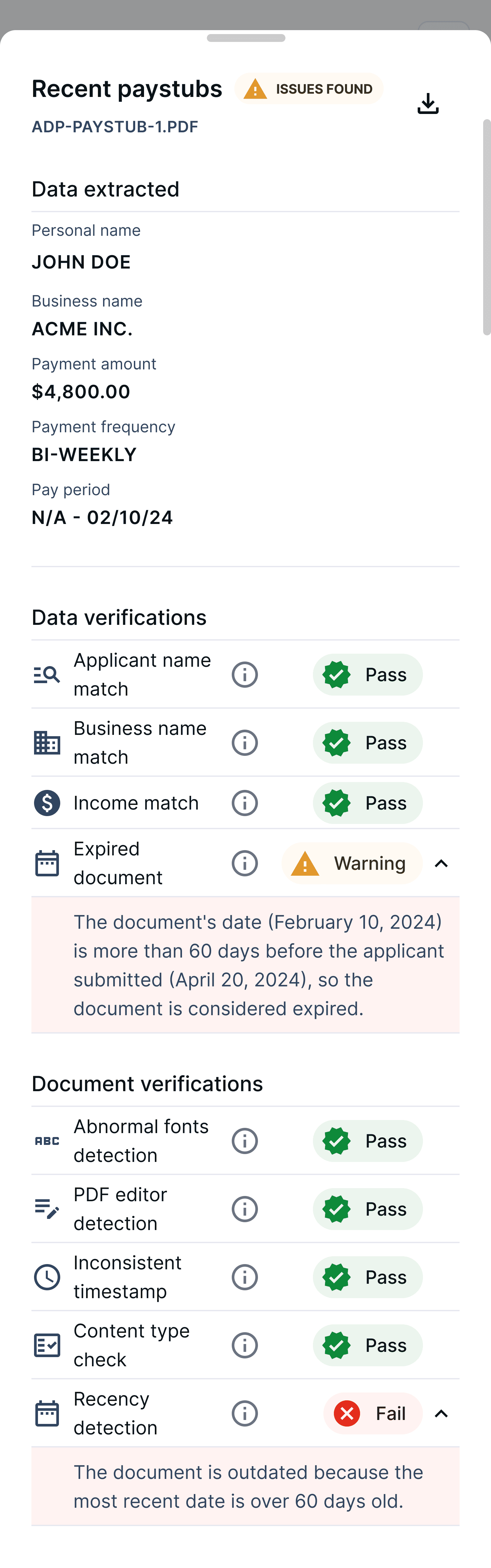
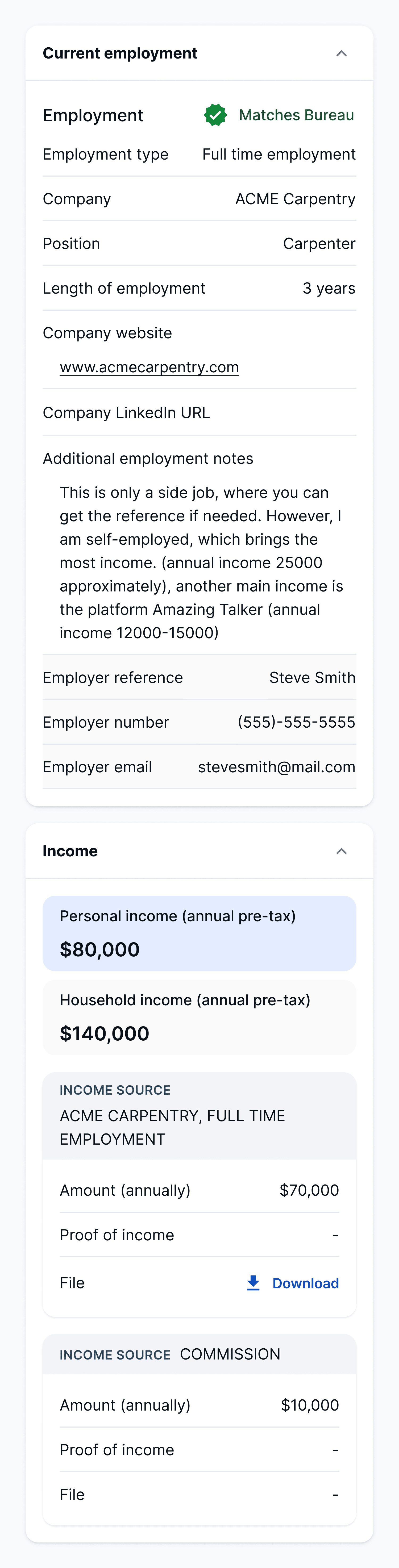
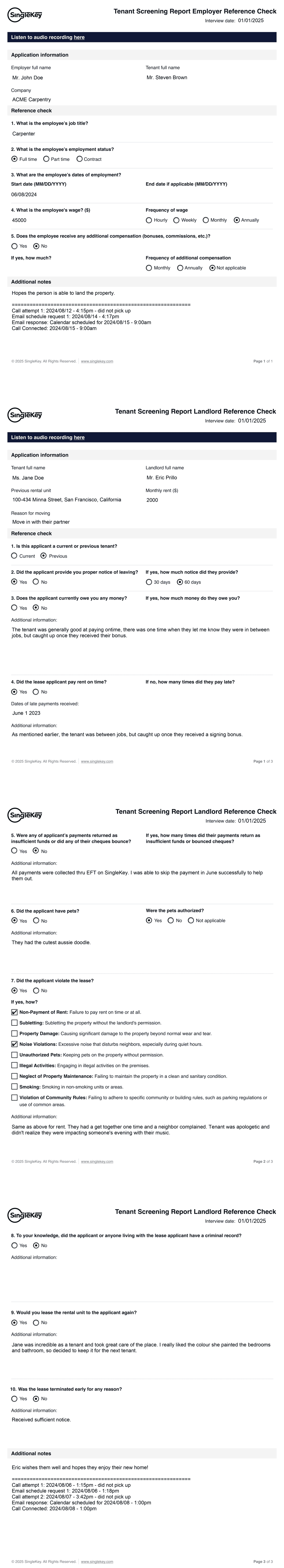

Combine a full credit check by Equifax with in-depth, employment and income info to get a comprehensive picture of your potential renters.

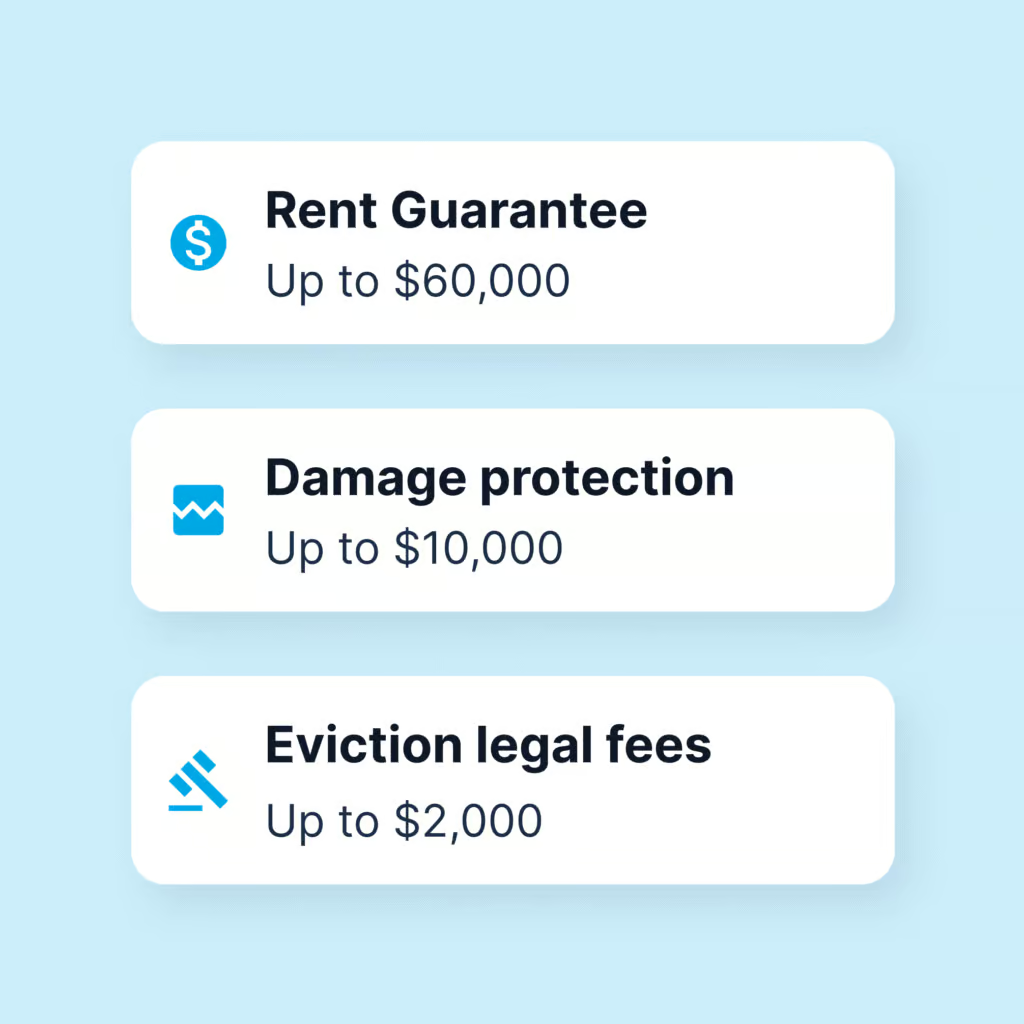
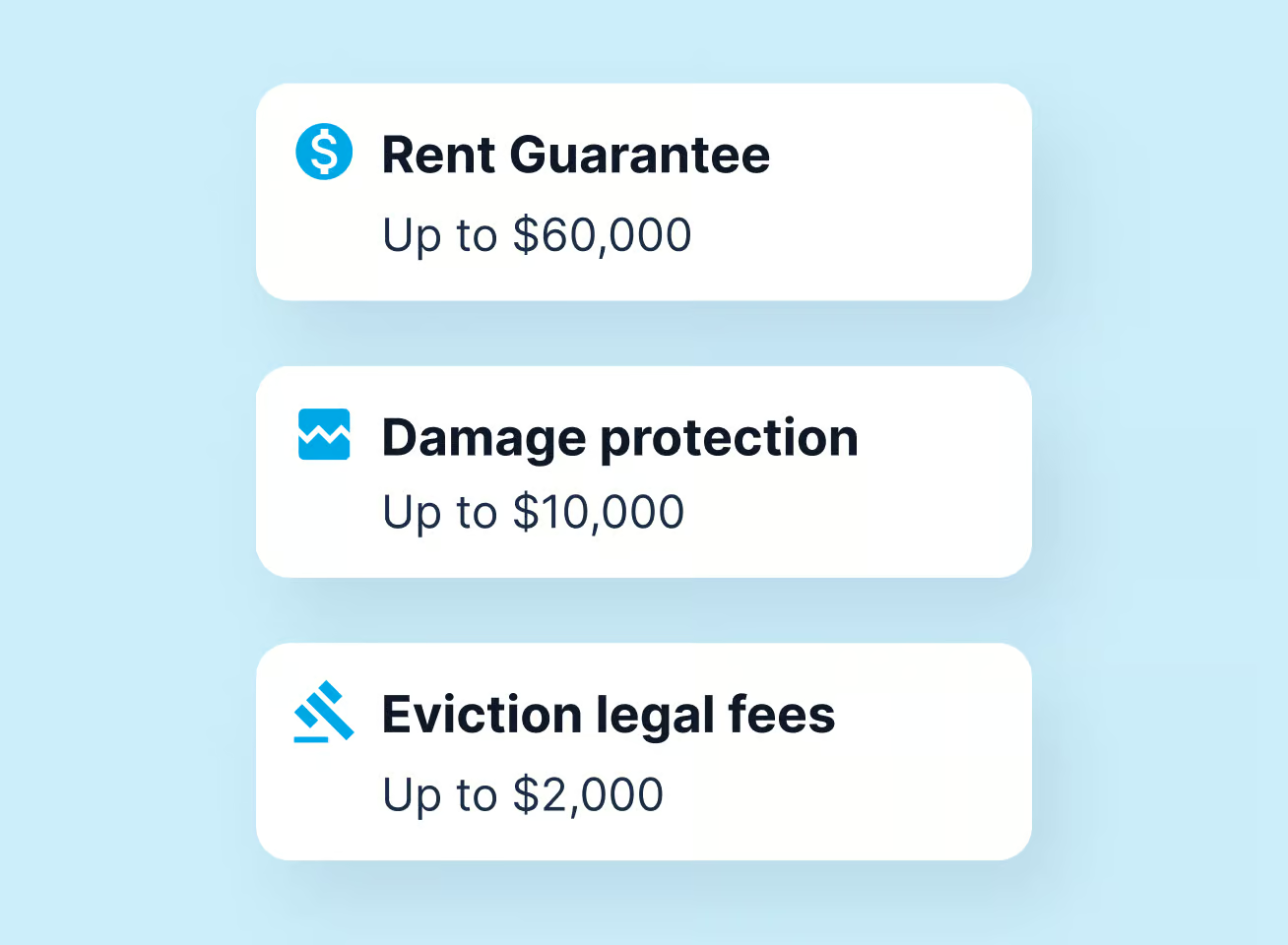

Stop worrying about having to pay a second mortgage. In case of missed rent payments, property damage, or an eviction, the Rent Guarantee takes on tenant risks and gives you financial and legal support.
Our integrated platform takes you from lead to lease. Collect, qualify, and manage your risks with SingleKey.
Stop worrying about having to pay a second mortgage. In case of missed rent payments, property damage, or an eviction, the Rent Guarantee takes on tenant risks and gives you financial and legal support.

Make tenant screening more efficient and focus on the property management tasks that help you operate your properties more profitably.

Protect your clients.

Stand out in a competitive rental market with guarantor services and a shareable rental application.

Homeowners
Real estate agents
Property managers
Tenants screened

Pre-screen interested leads by asking key questions before proceeding to viewings.
STARTING AT
/ report
Find your ideal tenant with a verified and comprehensive credit, rental, and employment history.
STARTING AT
/ monthly rent per tenant

have questions?
Our top-rated Customer Success Team is here to help. Our friendly representatives are dedicated to providing personalized support. Whether you have questions about our products or need technical guidance, we’re ready to assist. Live support hours are from 8 a.m. to 7 p.m. EST on weekdays and 10 a.m. to 2 p.m. EST on Saturdays.